Electromyogram and Nerve Conduction Study (EMG/NCS)
Why is this test performed?
Numbness, tingling, pain, muscle wasting or weakness in the body are the most common indications for the study. Typical conditions that require a nerve conduction study are: Spinal disc herniation, carpal tunnel syndrome, ulnar nerve neuropathy, peroneal neuropathy, tarsal tunnel syndrome, polyneuropathy due to diabetes and other metabolic and autoimmune conditions and Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Electrodiagnostic testing includes a range of specialized tests, including nerve conduction studies (NCS) and needle electromyography (EMG), that are used to evaluate the peripheral nervous system. This test is an extension of the physical examination, to provide sufficient and valuable information to establish a diagnosis of neuromuscular dysfunction of the peripheral nervous system or muscle disease.
The information these tests provide will allow physicians to create a treatment plan that addresses a patient’s specific symptoms.
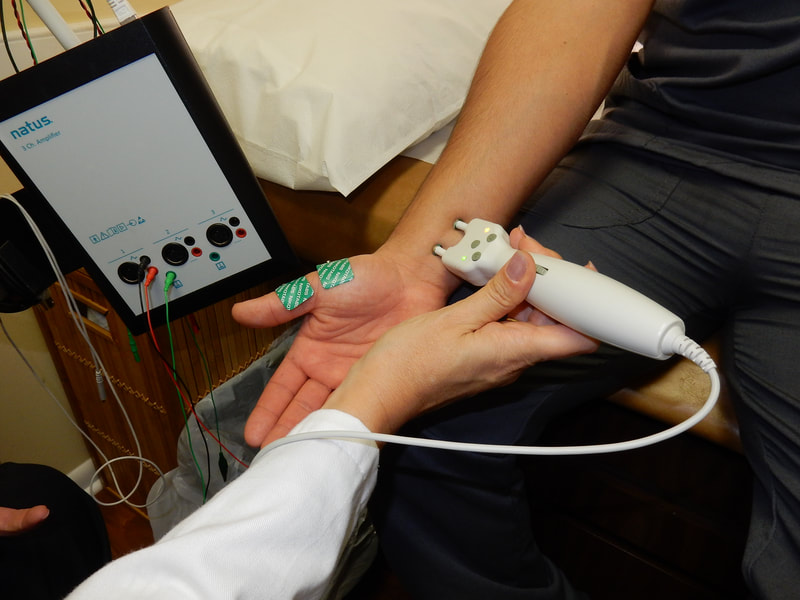
What is a Nerve Conduction Study?
For this test, a series of surface electrodes are placed at different locations along specific peripheral nerves. The nerve is stimulated at one site and recorded at a different site to determine if the nerve is conducting appropriately. Each electrical stimulation is recorded as a waveform on a computer and analyzed by the neurologist.
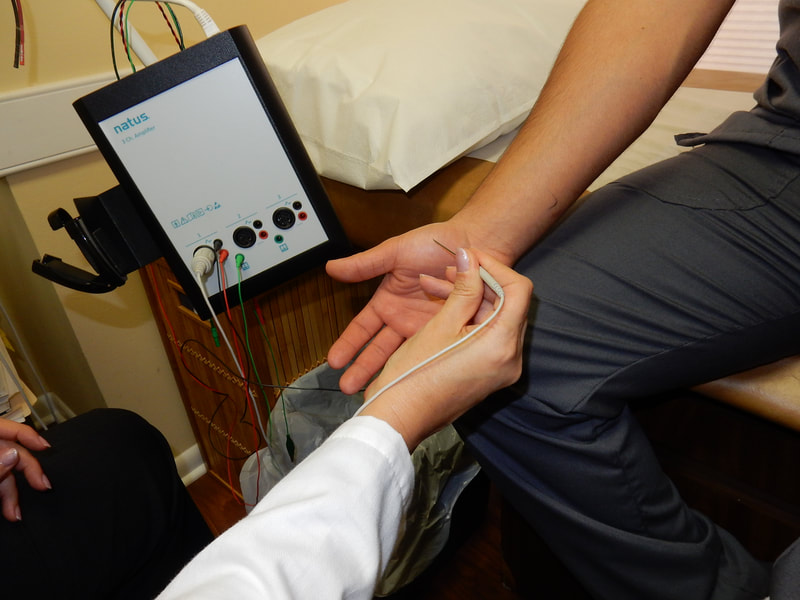
What is an Electromyogram (EMG)?
This portion of the test is used to assess both nerve and muscle functions. A small-diameter concentric needle is placed into a muscle to evaluate insertional activity, resting activity, voluntary recruitment, morphology, and size of motor units, as well as motor unit recruitment. The needle electrode examination provides valuable information about the electrical characteristics of individual muscle fibers and motor units, as well as the integrity and innervation of muscle fibers. This test can be uncomfortable for the patient.
Preparation and Instructions
Why is this test performed?
Numbness, tingling, pain, muscle wasting or weakness in the body are the most common indications for the study. Typical conditions that require a nerve conduction study are: Spinal disc herniation, carpal tunnel syndrome, ulnar nerve neuropathy, peroneal neuropathy, tarsal tunnel syndrome, polyneuropathy due to diabetes and other metabolic and autoimmune conditions and Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Electrodiagnostic testing includes a range of specialized tests, including nerve conduction studies (NCS) and needle electromyography (EMG), that are used to evaluate the peripheral nervous system. This test is an extension of the physical examination, to provide sufficient and valuable information to establish a diagnosis of neuromuscular dysfunction of the peripheral nervous system or muscle disease.
The information these tests provide will allow physicians to create a treatment plan that addresses a patient’s specific symptoms.
What is a Nerve Conduction Study?
For this test, a series of surface electrodes are placed at different locations along specific peripheral nerves. The nerve is stimulated at one site and recorded at a different site to determine if the nerve is conducting appropriately. Each electrical stimulation is recorded as a waveform on a computer and analyzed by the neurologist.
What is an Electromyogram (EMG)?
This portion of the test is used to assess both nerve and muscle functions. A small-diameter concentric needle is placed into a muscle to evaluate insertional activity, resting activity, voluntary recruitment, morphology, and size of motor units, as well as motor unit recruitment. The needle electrode examination provides valuable information about the electrical characteristics of individual muscle fibers and motor units, as well as the integrity and innervation of muscle fibers. This test can be uncomfortable for the patient.
Preparation and Instructions
- Bathe or Shower the day of your test
- Do not apply lotions, creams or oils to your skin
- Wear loose fitting clothing; shorts, if possible, especially if testing legs
- Advise the staff if you are taking blood thinners